Understanding Retatrutide for Weight Loss
Retatrutide is a novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist currently under investigation for its potential in weight management. Unlike some weight-loss medications that target a single pathway, retatrutide acts as a triple agonist, activating GLP-1R, GIPR, and GCGR receptors. This multi-pronged approach offers a unique mechanism of action: It modulates appetite, enhances satiety (feeling full), and improves glucose metabolism. However, it's crucial to remember that retatrutide is not a stand-alone solution; a healthy lifestyle, encompassing balanced nutrition and regular physical activity, remains paramount for optimal results. How effective is this approach in clinical trials? Let's explore the data.
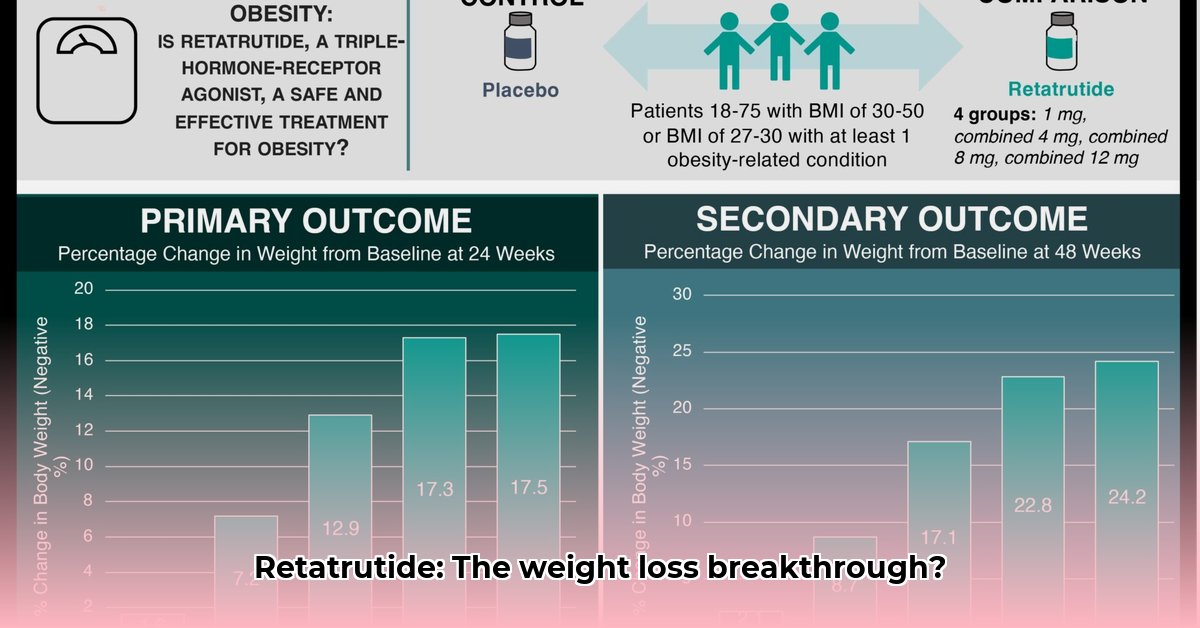
Retatrutide Dosage and Weight Loss: Clinical Trial Findings
Early-phase (Phase 2) clinical trials have demonstrated a compelling correlation between retatrutide dosage and weight loss. Higher doses were associated with greater weight reduction. Specifically, a once-weekly 12mg dose yielded a remarkable average weight loss of 24.2% in these trials. This substantial reduction suggests significant potential for individuals struggling with obesity. However, is this weight loss consistent across all participants? A remarkable 100% of participants in the 8mg and 12mg weekly dose groups achieved at least a 5% reduction in their initial body weight, highlighting a high rate of success within the study's parameters. Moreover, a subset of the 12mg group experienced an impressive 82.4% reduction in liver fat, suggesting potential benefits beyond weight loss, influencing overall metabolic health. Importantly, these results are based on controlled trial settings, and real-world outcomes may vary. What are the potential drawbacks?
Potential Side Effects of Retatrutide
While the efficacy of retatrutide is promising, it’s essential to acknowledge its potential adverse effects. Gastrointestinal issues, including nausea and diarrhea, are the most frequently reported side effects. The incidence of these side effects generally increases with higher doses, leading some participants to discontinue treatment. Although often manageable, careful consideration of these side effects is necessary. Less common, but more serious, adverse events such as pancreatitis and liver problems have also been reported, emphasizing the need for close medical monitoring. Ongoing Phase 3 trials are collecting vital long-term data on safety and efficacy, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the drug's risk-benefit profile. What are some practical steps to manage these challenges?
Managing Retatrutide Side Effects: A Practical Guide
The most common side effects associated with retatrutide are gastrointestinal in nature. These include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation, often appearing early in treatment and potentially lessening with time as the body adjusts. The severity of these side effects is often related to the dose administered. The following strategies can help mitigate gastrointestinal discomfort:
- Titration: Begin treatment with a low dose, gradually increasing it under your doctor’s supervision. This allows for gradual adaptation, minimizing the impact of side effects.
- Hydration: Maintain adequate hydration throughout the day. Proper hydration supports digestive function and can alleviate gastrointestinal distress.
- Dietary Modifications: Consult a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for guidance on dietary adjustments. Small, frequent meals can help improve tolerability.
- Medication Timing: Experiment with different times of day for medication administration. Taking retatrutide with food may alleviate nausea.
- Symptomatic Management: If necessary, utilize over-the-counter medications such as anti-nausea drugs, under the guidance of your healthcare provider. Avoid self-medication.
- Communication: Report any severe or persistent side effects to your doctor immediately. Open communication is crucial for timely intervention and treatment adjustments.
Beyond gastrointestinal symptoms, rarer but potentially serious side effects, including pancreatitis and liver dysfunction, require immediate medical attention. Continuous medical supervision, including regular blood tests, is essential to monitor liver function and overall health.
Conclusion: Informed Decision-Making with Retatrutide
Retatrutide shows considerable promise for weight loss, but its use requires careful consideration of both its benefits and risks. The information provided is for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication. They can assess your individual health status, evaluate your suitability for retatrutide, determine the appropriate dosage, and monitor you for any adverse effects. Remember, collaborative decision-making between you and your healthcare provider is crucial for navigating the path to successful weight management. The journey toward better health requires a tailored approach, and your doctor is your trusted guide.